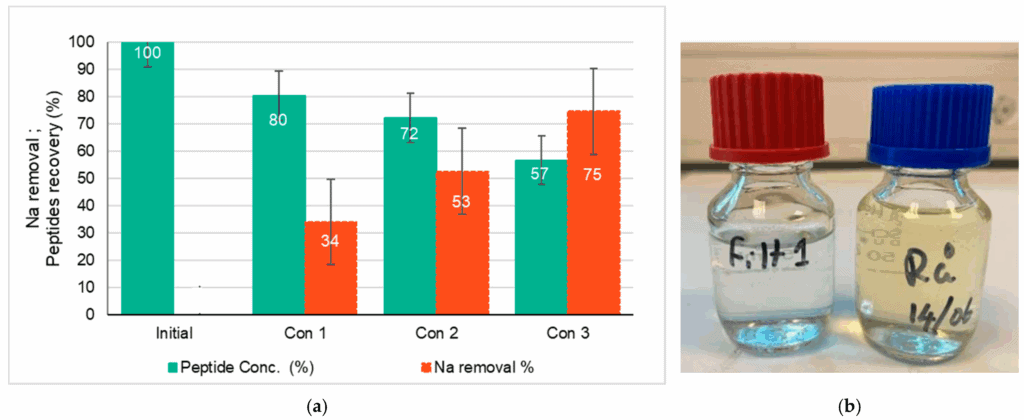
Crossflow membrane separation was used as a scalable downstream process for the up concentrate of low-molecular-weight peptides and for the removal of salt (NaCl) from Calanus finmarchicus hydrolysate. Membrane processes are increasingly used for various applications in both upstream and downstream processing. The C. finmarchicus hydrolysate was prepared by enzymatic hydrolysis, followed by crossflow separation. The stepwise membrane nanofiltration of hydrolysate contributed to a progressive reduction in salt in the hydrolysate. The salt concentration in the concentrates decreased by 34%, 53%, and 75%, highlighting the efficiency of the filtration process in separating NaCl from peptides. This gradual reduction in salt concentration suggests that the membrane effectively facilitated NaCl removal while retaining peptides. Briefly, 75% NaCl removal was achieved, with peptide recovery reaching 57% using an NFX membrane in crossflow filtration.
Read the full publication: Manamperuma, L.D.; Dibdiakova, J.; Kjønnø, O.; Rusten, B.; Matic, J.; Wubshet, S.G.; Vik, E.A. https://www.mdpi.com/3202292